Discovery and characterization of naturally occurring chalcones as potent inhibitors against bile salt hydrolases
Abstract
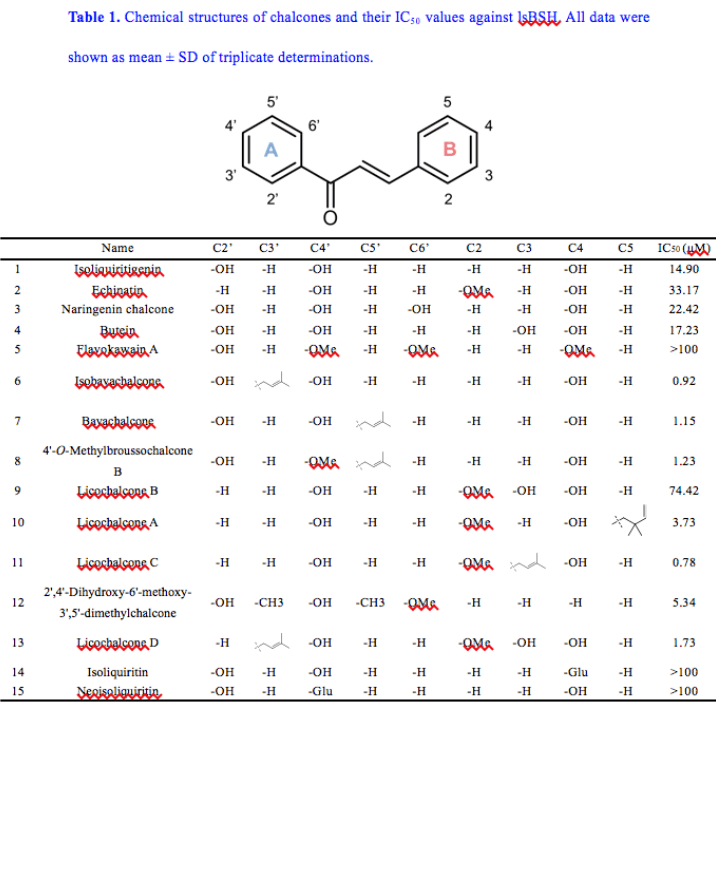
Bile salt hydrolases (BSHs) play crucial roles in deconjugation of the conjugated bile acids, have been recognized as key targets to modulate bile acid metabolism. This study aims to find efficacious BSH inhibitors from a natural compound library and to characterize the inhibitory mechanism of identified BSH inhibitors. Following assaying of the inhibition potentials of more than 100 natural compounds against BSH produced by Lactobacillus salivarius (lsBSH), several chalcones were found with strong or moderate lsBSH inhibition activity. Of all tested chalcones, licochalcone C and isobavachalcone displayed the most potent lsBSH inhibition activity (IC50 < 1 μM). Inhibition kinetic analyses demonstrated that both licochalcone C and isobavachalcone reversibly inhibited lsBSH-catalyzed CA-AMCA hydrolysis via a mixed inhibition manner. Docking simulations suggested that they could bind on lsBSH at two distinct sites mainly via hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions. Additionally, licochalcone C and isobavachalcone can inhibit various BSHs and reduce the total BSH activities in mice feces, suggesting that these agents are broad-spectrum BSH inhibitors. Collectively, our findings reveal that licochalcone C and isobavachalcone are naturally occurring inhibitors of BSH, and these two agents can be used as promising lead compounds to develop more efficacious BSH inhibitors for modulating bile acid metabolism.