Long-term Clinical Outcomes of Coronary Rotational Atherectomy for Specific Indications
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to compare the long-term outcomes between specific indications and on-label use of rotational atherectomy (RA) for severely calcified coronary lesions.
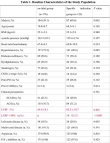
Methods: Data of patients treated for RA from 2015 to 2020 in a single-center registry were analyzed. The specific indication group included patients with ostial lesions, unprotected left main coronary artery stenosis, chronic total occlusions, stent ablation, angulated lesions, and cardiac dysfunction, whereas patients who had none of the above-mentioned characteristics were included in the on-label group. The primary endpoint between groups were compared.
Results: 176 patients in the on-label group and 125 patients in the specific indication group were included. Clinical characteristics were comparable between groups. The incidence of complications during the procedure was higher in the specific indication group than in the on-label group (20.0% vs. 10.8%, P=0.018). There was no significant difference in in-hospital MACCE between groups (12.5% vs 9.7%, P=0.392). During 35 (10-57) months of follow-up, MACCE occurred in 46 patients (15.3%). The incidence of MACCE was much higher in the specific indication group than in the on-label group (25.6% vs 13.6%, P=0.034).
Conclusions: RA for specific indications had a higher incidence of complications during the procedure and poor long-term clinical outcomes.