Molecular mechanism of transporter regulation and their impairment in intrahepatic cholestasis
Abstract
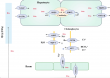
Intrahepatic cholestasis (IC) is a liver disease caused by bile formation and excretion disorders due to structural and functional abnormalities of hepatocytes and/or bile capillary. It is commonly caused by hepatitis virus, alcohol, drug-induced liver damage, autoimmune liver disease and heredity. If patients with IC do not receive effective treatment, IC can progress to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and ultimately liver failure. However, the mechanism of IC is still poorly understood. It is thought that IC is closely related to changes in the transcription, function and localization of hepatocellular transport proteins. To better understand the molecular mechanism of transport proteins in IC, we reviewed the roles of these transport proteins and discussed the underlying regulation mechanism of them in IC, aiming to provide a valuable reference for understanding its pathogenesis and developing effective drug therapies.