Predictive value of the combination of age, creatinine, and ejection fraction (ACEF) score and Fibrinogen in patients with acute coronary syndromes undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to explore whether the FIB can improve the predictive value of ACEF in patients with ACS.
Methods: A total of 290 ACS patients were enrolled in this study. The clinical characteristics and MACE was recorded.
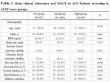
Results: Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that the level of FIB (Odds Ratio =7.798, 95%CI,3.44-17.676, P<0.001) and SYNTAX score (Odds Ratio =1.034, 95%CI,1.001-1.069, P=0.041) emerged as independent predictors for MACE. On the basis of the regression coefficient of FIB, the ACEF-FIB was developed. The area under the ROC of the ACEF-FIB scoring system in predicting MACE after PCI was 0.753 (95%CI 0.688-0.817, P<0.001), higher than the ACEF score, SYNTAX score and Grace score (0.627, 0.637 and 0.570 respectively).
Conclusion: Compared with other risk scores, the ACEF-FIB also had better discrimination ability based on ROC curve analysis, net reclassification improvement and integrated discrimination improvement.