Supplementary Material
Design and synthesis of novel hydroxamic acid derivatives based on quisinostat as promising antimalarial agents with improved safety
Preprint |
10.55415/deep-2022-0024.v1
This is not the most recent version. There is anewer
versionof this content available.
Abstract
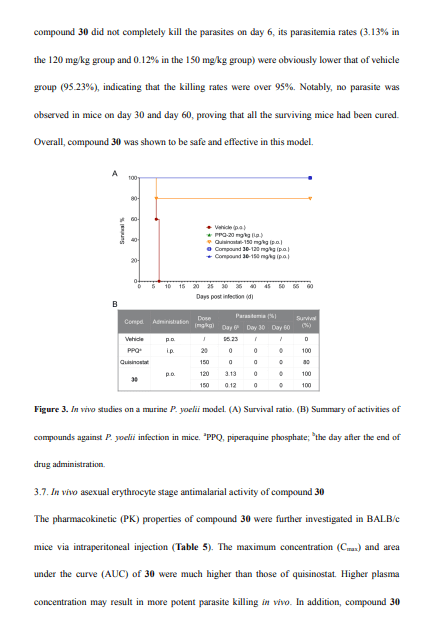
In our previous work, the clinical phase II HDAC inhibitor quisinostat was identified as a promising antimalarial agent through drug repurposing strategy, but its safety was of concern. Herein, further medicinal chemistry method was used to find new chemical entities with greater effectiveness and security than quisinostat. Totally, 38 novel hydroxamic acid derivatives were designed and synthesized and their in vitro antimalarial activities were systematically investigated. These compounds showed inhibitory effect on wild and drug-resistant Plasmodium falciparum strains in erythrocyte stage at nanomole concentrations. Among them, compound 30 displayed completely elimination of parasites in Plasmodium yoelii infected mice through oral administration, and also exhibited better safety and metabolic properties compared with our previous work. Moreover, compound 30 was proved that can upregulate the acetylation level of plasmodium histone by western blot, suggesting it exerted antimalarial effect by the inhibition of PfHDAC enzymes.