Silybin exerts therapeutic efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting Skp2
Abstract
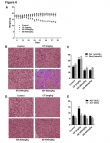
Silybin (SB), a natural flavonoid isolated from Silybum Marianum, has been clinically used to treat hepatic fibrosis and also used as a dietary supplement owing to its hepatoprotective potentials. Numerous studies have shown that SB also exerts promising anticancer property; however, the anticancer targets of SB and the underlying mechanism remain unclear. In our study, we found that SB significantly inhibited the proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), without causing cytotoxicity toward normal bronchial epithelial cells Beas-2B. Mechanistically, SB can bind to F-box protein Skp2 and disrupt Skp1-Skp2 interaction, thereby decreasing the protein level of Skp2 and inducing the accumulation of its substrates, leading to cell-cycle G1 phase arrest and cell migration suppression. In lung orthotopic xenografts, SB also significantly decreased Skp2 expression while increased p27/Kip1 (p27) protein level. SB administration inhibited tumor growth and metastasis in the lung tissue, prolonging the survival time of the mice without causing obvious toxicity. Taken together, SB can be considered a Skp2-targeting agent that warrants further clinical investigation.